| (Service Hotline) 0519-86365509 |
Contact: Shi Lijie +86 15851987186 (same number on WeChat)
Shi Jianlin +86 13806110378 (WeChat account)
Q Q: 657352779
Production room telephone: +86 519-86358076
General Manager Tel: +86 519-86365509
Fax: +86 519-86365069
E-mail: 657352779@qq.com
Website: en.czxmzc.com
Address: No. 98, Weijiaqiao, Niutang Industrial Park, Wujin District, Changzhou City
Roller bearing is a kind of bearing that uses two rolling elements (such as balls or rollers) as a race to carry load between the bearing rings. The relative movement of the seat ring causes the rolling elements to roll with little rolling resistance and small sliding.
One of the famous roller bearings is a log laid on the ground with a large rock on top. When the stone is pulled, the log rolls along the ground with almost no sliding friction. When each log comes out from the back, it moves to the front, and then the block rolls on it. This type of bearing can be imitated by placing a few pens or pencils on the table and placing objects on top of them. For more information about the historical development of bearings, see "Bearings".
Rolling element rotary bearings use shafts in larger holes, and cylinders called "rollers" tightly fill the space between the shaft and the holes. In the above example, as the shaft rotates, each roller acts as a log. However, because the bearings are round, the rollers will never fall under the load.
The advantage of roller bearings is that they can be a trade-off between cost, size, weight, load-bearing capacity, durability, precision, friction and so on. Other bearing designs usually perform better on a specific property, but perform poorly on most other properties, although fluid bearings may sometimes simultaneously perform well in terms of load carrying capacity, durability, accuracy, friction, rotation rate, and sometimes cost. . Only sliding bearings are widely used as roller bearings. Common mechanical components that are widely used are-automotive, industrial, marine and aerospace applications. They are a necessity of modern technology. Rolling bearings are developed on a solid foundation for thousands of years.
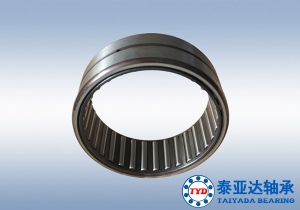
Roller bearing is a very common rolling bearing. The bearing has an inner ring and an outer ring, and the balls roll between them. Each race has a groove that usually has a certain shape, so the ball is slightly loose. Therefore, in principle, the ball touches each race in a very narrow area. However, a load on an infinitely small point will result in an infinitely high contact pressure. In practice, the ball deforms (flattens) slightly when it touches each race, just like a tire flattens when it touches the road surface. The game also yielded slightly where each ball pressed against it. Therefore, the contact between the ball and the race has a limited size and has a limited pressure. The deformed ball and seat ring cannot roll completely smoothly because different parts of the ball move at different speeds when rolling. Therefore, there are opposing forces and sliding motions at each ball/ring contact. Overall, these will cause bearing resistance.
The length of the cylinder used in ordinary roller bearings is slightly longer than the diameter. Roller bearings generally have a higher radial load capacity than ball bearings, but have lower loads and greater friction under axial loads. If the inner race and outer race are not aligned, the bearing capacity will usually drop rapidly compared to ball bearings or spherical roller bearings.
As with all radial bearings, the external load is constantly redistributed between the rollers. Usually, less than half of the total number of rollers bear a large part of the load. The animation on the right shows how the bearing rollers bear static radial loads when the inner ring rotates
